Is Low-Dose Naltrexone an Option for my Condition?
- By Dr. Shannon Evans, DO, IFMCP
- •
- 13 Nov, 2020
- •

THE BASICS:
Low-Dose Naltrexone otherwise known as LDN is a compounded medication that has been shown to help balance out ticked off or dysregulated immune systems.
Common Conditions treated with LDN:
✅ Hashimoto’s (autoimmune thyroid disorder)
✅ Fibromyalgia
✅ Crohn’s Disease
✅ Ulcerative colitis
✅ Multiple Sclerosis
✅ Autism
✅ Irritable bowel syndrome and other gastrointestinal disorders
✅ Rheumatoid arthritis
✅ Systemic Lupus Erythematosus
✅ Multiple Chemical Sensitivity
✅ Chronic pain
✅ Cancers and so much more….
Not all conditions listed above have had published clinic studies. Research continues to be ongoing with different conditions. Currently there is a study being conducted on LDN for treatment of COVID positive patients.
Research into the effects of LDN is ongoing and not a new venture. Research into LDN started in the mid-1980’s for treating HIV patients.
How Does LDN work?
THE GENERAL SCIENCE:
- LDN is a competitive opioid antagonist. In large dose, naltrexone blocks the effects of both endogenous opioids (made by the body) and pharmaceutical opioids (opioid medications).
- LDN is a pure inhibitor. The structure of LDN looks very similar to endorphins that are produced naturally by the body, called met-enkephalin, otherwise known as opioid growth factor.
- LDN is an antagonist at the opioid growth factor receptors. A variety of human cells have opioid growth factor receptors.
- LDN binds to endorphin receptors & the blockade lasts ~4-6 hours, which can cause analgesia and anti-inflammatory effects in part due to the increased production of the body’s endorphins.
To understand how LDN is working with the body, first, we need to understand what ENDORPHINS are:
The body makes endorphins to help regulate cell growth, including immune cells. Many patients with autoimmune disease tend to have low levels of endorphins, which is important for regulating the body’s immune system.
Opioid receptors are located throughout the body including the digestive system, nervous system and on certain immune cells.
THE SPECIFICS:
Low dose naltrexone binds to opioid receptors causing the body’s endorphins to be displaced or removed from the OGF receptors. This affect causes the body’s cells to become deficient or lacking in OGF (also known as endorphins). The body compensates by:
1️⃣ Producing more OGF receptors to get more OGF (endorphins) to bind to the cells
2️⃣ Sensitivity of the OGF receptors become more sensitive to try and get more OGF (endorphins) to bind to the cells
3️⃣ Production of OGF (endorphins) increases to try and compensate for the perceived deficient of OGF.
In a Nutshell:
If a patient takes LDN, they receive a brief blockade of the OGF receptors for a few hours, causing a rebound effect of increased endorphins and increasing the production and sensitivity of OGF (endorphins) and OGF receptors. Once the LDN has been metabolized by the liver, the high level of endorphins produced by this rebound effect can then interact with OGF receptors and assist in regulating the body’s immune system and cell growth.
HOW TO TAKE LDN:
Low dose naltrexone has shown to be beneficial at 4.5 mg in studies. However, every individual is unique, so I take a more individualized approach. I have found that lower doses for some individuals is just as beneficial. With all patients, starting out at a lower dose and working up to an individual’s therapeutic dose is key. Most research recommends starting at 0.5 mg up to 1.5 mg. Depending on the individual, certain patients may need to start out on a smaller dose and their therapeutic dose may be lower than 4.5 mg.
LDN is ideally taken at bedtime, which allows LDN to be most potent when the body’s endorphin levels should be highest.
WHO CAN TAKE LDN:
LDN has been studied on adults and children as young as 4 years old.
DIFFERENT FORMS OF LDN:
The most common form of LDN prescribed are tablets or capsules, which are available by prescription from a compounding pharmacy.
LDN can also be in liquid formulations, sublingual drops, eye drops, creams and lotions.
POTENTIAL SIDE EFFECTS OF LDN:
- Most individuals, in my experience, don’t experience any side effects with LDN.
- Some individuals may have disturbed sleep for a few days when first starting LDN. If disturbed sleep continues, switching LDN to a daytime dose may be helpful.
- Some individuals may have vivid dreams
- Rarely nausea, constipation or diarrhea. If GI side effects occur, it may be helpful to switch to sublingual or topical forms of LDN to bypass the gut.
MY THOUGHTS ON LDN:
LDN can be a very useful medication in helping an individual get a ticked off immune system balanced, which can make it easier to work with patients on fixing the root cause of their issues.
Since I partner with a lot of patients that can’t tolerate any medications, supplements, have trouble living in their environment by reacting to many foods and their environment. The patient’s immune system needs assistance with balance and decreased inflammation, before work can begin on the root causes of issues.
In my opinion, LDN is not a magic pill or a cure—it is a tool to help an individual become more comfortable with less pain, being able to better tolerate their environment by helping out a dysfunctional immune system.
I have patients that have benefited from LDN who have Hashimoto’s, Multiple Sclerosis, Multiple Chemical Sensitivities, Ulcerative Colitis, Fibromyalgia, Chronic migraines to name a few…
If you or a loved one would like to learn more about LDN and if it is a possibility to help in your journey to optimal health, schedule a FREE 15 minute consult with New Beginnings. To schedule call 970-305-0101 or email Staff@NewBeginningsFMC.com.
References:
https://www.ldnscience.org/ldn
https://www.naturalmedicinejournal.com/journal/2018-04/uses-low-dose-naltrexone-clinical-practice

What is the Function & Importance of Your Gut?
First, let’s talk about some specifics of your digestive tract:
- The mouth is the beginning of your digestive tract, where the breakdown of food begins.
- Esophagus starts in your throat and receives food from your mouth when you swallow. It delivers food to your stomach due to a series of muscle contractions known as peristalsis.
- Stomach is a hollow organ that receives & holds the food that is brought from the esophagus. Stomach produces or makes stomach acid to help break down food, and kills pathogens (bacteria, fungus & parasites) that can cause harm to your body.
- Small intestines then receive the stomach contents. Food continues to break down from enzymes released by the pancreas and liver. A series of muscle contractions otherwise known as peristalsis occurs to move food through and mix the food with the digestive enzymes.
- Pancreas secretes digestive enzymes into the first part of the small intestine called the duodenum. It also secretes insulin to metabolize sugar.
- Liver has lots of important functions! It helps with digestion from nutrients absorbed from the small intestine. The liver also makes bile which breaks down fats that are ingested. It also helps to detoxify potentially harmful chemicals (converts toxic substances into harmless substances).
- The gallbladder stores the bile that is made by the liver. It releases bile into the small intestine when you eat fat to help absorb and digest fats.
- Colon or large intestine processes waste. Most of your microbiome is located here!
Next, let’s dive a little deeper into the microbiome , to discuss it’s function and importance…
What is a microbiome? It is genetic material of all the microbes (bacteria, fungi, protozoa & viruses) that live on and inside the human body.
- You are mostly made up of microbes—over 100 trillion. Microbes outnumber your human cells 10 to 1.
- The majority of microbes live in your large intestine.
- Microbiomes can weigh up to as much as 5 pounds!
- What happens with the microbiome? Short chain fatty acids are produced when fiber is fermented in the colon, and these short chain fatty acids are a source of energy for your cells lining the colon. They also metabolize or breakdown foreign substances, certain drugs or chemicals the body does not recognize.
What is the link between your gut & immune system?
Did you know that the majority of your immune system is located in your GUT?
Gut-associated lymphoid tissue or GALT for short makes up 70% of your entire immune system!
This is why your gut plays a central role in your immune health and having a balanced immune system! The GUT is your GATEWAY to Health!
Understanding Inflammation:
Acute or short term inflammation is a part of your body’s appropriate immune system response to an acute injury or illness that is helpful for healing.
Acute inflammation is also an important defense against pathogens (harmful bacteria, parasites or viruses).
Your immune system’s ability to mount an adequate and appropriate inflammatory response is critical for survival! As an example, if you were to cut open your hand, causing a large open wound; you don’t want to have excessive bleeding or get an infection. When acute inflammation takes place due to this trauma—it helps you to clot—stopping the bleeding or decreasing the bleeding. It also takes care of pathogens that there is no longer a barrier against—so you don’t get an infection and then helps to heal your open wound. All which is appropriate and necessary! A balanced immune system is self-limited, beneficial and necessary!
Just to summarize, a balanced immune can identify potentially harmful pathogens or substances, recognize self, assess potential level of threat posed by infectious, toxic or non-self antigens and repair any damage that happens when the immune system takes care of threats.
What about Chronic Inflammation or an Unbalanced Immune System ?
Chronic inflammation happens when there is loss of balance of the immune system causing constant inflammation and destruction to your body.
Long term or chronic inflammation can lead to long term problems such as obesity, thyroid issues, autoimmune conditions, diabetes, heart disease and so much more!
Your immune system is no longer regulated and is out of control!
What are some ways gut issues lead to chronic inflammation?
- Issues with digestion . One of the most common digestive problems is not making enough stomach acid. Are you taking any medications that decrease stomach acid such as proton pump inhibitors (omeprazole, esomeprazole, lansoprazole) or H2 blockers (ranitidine, famotidine, cimetidine)?
- Remember that stomach acid is important for helping with the breakdown of food and killing pathogens such as bacteria, fungus & parasites.
- If you are not making enough stomach acid to help with the break down of food and also let bad bacteria, fungus or parasites survive to hang out in your intestines, which wreaks havoc & causes inflammation!
2 . Leaky Gut also known as intestinal hyperpermeability. This is when the intestinal lumen no longer has tight junctions between your cells. This means that the physical barrier between the digestive tract and blood stream is broken down; making it easy for intestinal contents to enter the blood stream.
- Your immune system will see things that it is not suppose to, such as big food particles, which causes your immune system to react. This can then lead to food sensitivities for example.
- Your immune system will also be exposed to more pathogens.
How Does Leaky Gut Happen?
- NSAIDs such as ibuprofen, steroids, and naproxen. Research shows that NSAIDs cause small intestinal inflammation causing leaky gut and can also be toxic to the cells of your gut.
- Viral, bacterial or protozoan infections
- Gluten
- Inflammation
- Stress
- Cytotoxic drugs
- Xenobiotics such as glyphosate which alters the gut microbiome
- Heavy metals such as mercury
- Antibiotics which alter the microbiome
- Standard American Diet
Chronic Health Issues associated with gut health : If your gut is ticked off, your immune system is gonna be ticked off, causing chronic inflammation that affects your whole body!
Everyone has different genetics and environmental factors, which can lead to a different path of chronic issues you are faced with!
Obesity . Defined as “accumulation of abnormal or excessive fat that may interfere with the maintenance of an optimal state of health.” In the U.S. the population with obesity is 42.2%. There is not any up to date costs for obesity, but in 2008 the estimated annual cost was $147 billion dollars. This was 12 years ago, and now the percentage of obesity has increased from 2008. Can you imagine what the annual cost is now?
Chronic inflammation causes an increase in certain inflammatory mediators (such as TNF-alpha, IL-6) which can lead to inflammation in fat cells (adipose tissue).
Did you know that fat cells (white adipose tissue) is an active participant in regulating your immune system and play a role in inflammation?
Fat cells (adipose tissue) that are exposed to chronic inflammation initially from the gut can then go on to produce more inflammation, which ends up becoming a vicious cycle.
When fat cells become enlarged, the blood supply to these cells may be decreased leading to a limited blood supply to this tissue. When this happens, fat cells or tissue begin to die, which leads to more production of inflammatory mediators! This then leads to overall inflammation in the body that is linked to:
- Abdominal obesity
- Metabolic abnormalities that lead to altered cholesterol and sugar metabolism
- Atherosclerosis than can lead to heart attacks and stroke
- Insulin resistance
- Diabetes
- High blood pressure
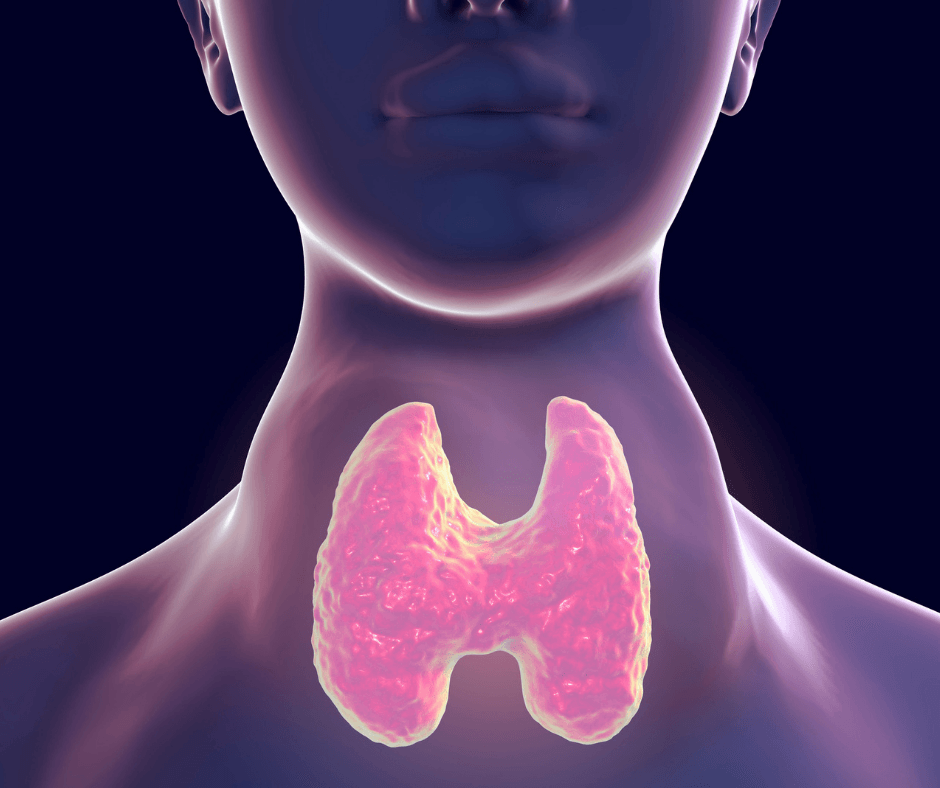
Thyroid issues. To really understand why thyroid problems are a big deal, first we must understand the importance of a well functioning thyroid. The thyroid is a small, butterfly-shaped gland located at the base of the neck. It may be small, but it is powerful and plays a vital role in how your body functions! The thyroid can influence all the parts of your body such as your gut, heart, brain, liver, kidneys and much, much more!
Your thyroid needs proper fuel or nutrients to produce thyroid hormone to be able to influence the rest of your body.
The thyroid gland mostly produces T4 (thyroxine) and some T3 (triiodothyronine) that is made up of iodine and tyrosine. T4 contains four iodine atoms and T3 contains three iodine atoms. Conversion of T4 to T3 takes place mostly outside of the thyroid gland. Most of the body responds & recognizes T3.
If the gut is in poor condition, such as a leaky gut, it is going to be difficult to get nutrient absorption to take place from the gut into the rest of the body. The thyroid suffers and does not get all the vital nutrients such as iodine and selenium for proper functioning.
Why else is having a healthy gut important for your thyroid health?
- 20% of the conversion of T4 to T3 happens in the gut!
- Healthy gut microbes can convert T4 to T3.
- Bile acids when secreted into the small intestine following fat consumption increase activity of the enzyme that converts T4 to T3.
Hashimoto’s is an autoimmune disease that affects more women than men. Hashimoto’s is a chronic inflammatory state in which the immune system makes antibodies that attack the thyroid gland. This then damages the thyroid, and if left untreated, can lead to the thyroid not making enough thyroid hormones. If found and treated early, most individuals with Hashimoto’s will not need to be on thyroid replacement medication.
Autoimmune Conditions can occur other places in the body, not just the thyroid. Autoimmune conditions are a result of the immune system attacking the body’s own organs, tissues and cells.
- Affects 23.5 million U.S. citizens
- Leading cause of death & disability
- More than 80 diseases are associated with autoimmune conditions
- Most common: Hashimoto’s, Lupus, Inflammatory Bowel Disease, Rheumatoid Arthritis, Multiple Sclerosis, Type 1 Diabetes, Grave’s Disease, Celiac disease
- Inflammatory bowel disease is chronic inflammation of the GI tract. Prolonged inflammation results in damage to the GI tract. Two types of IBD: Crohn’s disease and ulcerative colitis. Crohn’s disease can affect all parts of the GI tract—mouth to anus. Inflammation may include multiple layers of the walls of the GI tract. Ulcerative colitis affects the large intestine and rectum. Damage is usually patchy. Inflammation is usually present in the innermost layer of the lining of the colon.
Chronic inflammation from leaky gut can also cause seasonal allergy symptoms to be out of control!
Six STEPS to a Healthy Gut & Balanced Immune System:
- Eat a clean, well-balanced diet
- Eat earth made foods. Earth made foods don’t need labels! Try to eat a rainbow of colors in regards to produce to get all your nutrients—each color has different minerals, vitamins etc.
- Stay away from processed foods such as soda and box foods that can cause inflammation. If you are reading ingredients labels and see a big, long word that you have no idea how to pronounce or what it is, your body likely has no idea what it is either, so your immune system mounts a response causing inflammation!
- Buy organic foods. If the budget does not allow for all organic foods, buy all the produce that are listed under the Dirty Dozen organic. The Environmental Working Group has a list of produce with the highest pesticide/herbicide contents: www.EWG.org (strawberries, spinach, kale, nectarines, apples, grapes, peaches, cherries, pears, tomatoes, celery, potatoes, and hot peppers).
2. Stay well-hydrated with water
- Most of your body is made up of water and needs water to work effectively and also flush out toxins.
- In general, drinking 1/2 your weight in ounces per day is enough. For example, a 150 lb person needs ~75 oz of water daily. You may need more water if you are out in the sun or exercising vigorously!
- Also something to consider is how your water rate? What is your water source? How clean is your water? Have you considered filtered water?
3. Rest
- Are you getting quality sleep at night?
- How many hours of sleep do you get at night?
- Do you wake up well rested?
- Sticking to a schedule can be very helpful: going to bed and getting up at the same time everyday.
4. Self care
- Are you taking time daily for yourself?
- Are you taking time to rest and let your body reset?
- Are you taking time for movement or exercise?
- Self care looks different for everyone. Self care is a way for you to relax and do something you enjoy!
5. De-Stress
- This is a part of self care. You need to find ways to stay calm and relaxed.
- Chronic stress all by itself causes inflammation!
- If you have trouble taking time for yourself here are some tips: put self care on your daily schedule—even if it is for 2-5 minutes to start out. Have an accountability partner to make sure you are not ignoring your scheduled self care!
6. Supplements
- Multivitamin: basic minerals and vitamins that your entire body needs to function daily.
- Omega 3’s: anti-inflammatory for your gut and whole body. Your body needs omega 3’s to make cell membranes, make hormones and fuel your brain.
- Probiotics: improve gut health—digestion, absorption and microbiome. Also helps to improve immune health.
Having gut issues or an out of whack immune system? Need a partner in your health journey? Schedule a FREE 15 minute strategy call with New Beginnings. Email Staff@NewBeginningsFMC.com or call 970-305-0101 to schedule.
References:
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4566439/--role of gut microbiome
- https://depts.washington.edu/ceeh/downloads/FF_Microbiome.pdf--human microbiome
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5507106/
- https://www.cdc.gov/obesity/data/adult.html
- https://journal-inflammation.biomedcentral.com/articles/10.1186/1476-9255-9-1
- https://www.niaid.nih.gov/diseases-conditions/autoimmune-diseases
- https://www.womenshealth.gov/a-z-topics/autoimmune-diseases
- https://www.cdc.gov/ibd/what-is-IBD.htm
- https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/inflammatory-bowel-disease/symptoms-causes/syc-20353315?p=1
- https://www.hsph.harvard.edu/nutritionsource/what-should-you-eat/fats-and-cholesterol/types-of-fat/omega-3-fats/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/16829066
- https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/articles/7041-the-structure-and-function-of-the-digestive-syst...
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/20351569
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/12269922
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/1555538
- https://academic.oup.com/intimm/article/8/2/231/671078
- https://ec.bioscientifica.com/view/journals/ec/6/4/R52.xml
- https://academic.oup.com/jcem/article/92/11/4180/2598186
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK279393/
- http://www.vivo.colostate.edu/hbooks/pathphys/digestion/basics/gi_immune.html
- https://www.thyroid.org/hypothyroidism/
- https://www.thyroid.org/hyperthyroidism/
- https://www.health.harvard.edu/vitamins-and-supplements/health-benefits-of-taking-probiotics
Dr. Shannon's Blog

What is the Function & Importance of Your Gut?
First, let’s talk about some specifics of your digestive tract:
- The mouth is the beginning of your digestive tract, where the breakdown of food begins.
- Esophagus starts in your throat and receives food from your mouth when you swallow. It delivers food to your stomach due to a series of muscle contractions known as peristalsis.
- Stomach is a hollow organ that receives & holds the food that is brought from the esophagus. Stomach produces or makes stomach acid to help break down food, and kills pathogens (bacteria, fungus & parasites) that can cause harm to your body.
- Small intestines then receive the stomach contents. Food continues to break down from enzymes released by the pancreas and liver. A series of muscle contractions otherwise known as peristalsis occurs to move food through and mix the food with the digestive enzymes.
- Pancreas secretes digestive enzymes into the first part of the small intestine called the duodenum. It also secretes insulin to metabolize sugar.
- Liver has lots of important functions! It helps with digestion from nutrients absorbed from the small intestine. The liver also makes bile which breaks down fats that are ingested. It also helps to detoxify potentially harmful chemicals (converts toxic substances into harmless substances).
- The gallbladder stores the bile that is made by the liver. It releases bile into the small intestine when you eat fat to help absorb and digest fats.
- Colon or large intestine processes waste. Most of your microbiome is located here!
Next, let’s dive a little deeper into the microbiome , to discuss it’s function and importance…
What is a microbiome? It is genetic material of all the microbes (bacteria, fungi, protozoa & viruses) that live on and inside the human body.
- You are mostly made up of microbes—over 100 trillion. Microbes outnumber your human cells 10 to 1.
- The majority of microbes live in your large intestine.
- Microbiomes can weigh up to as much as 5 pounds!
- What happens with the microbiome? Short chain fatty acids are produced when fiber is fermented in the colon, and these short chain fatty acids are a source of energy for your cells lining the colon. They also metabolize or breakdown foreign substances, certain drugs or chemicals the body does not recognize.
What is the link between your gut & immune system?
Did you know that the majority of your immune system is located in your GUT?
Gut-associated lymphoid tissue or GALT for short makes up 70% of your entire immune system!
This is why your gut plays a central role in your immune health and having a balanced immune system! The GUT is your GATEWAY to Health!
Understanding Inflammation:
Acute or short term inflammation is a part of your body’s appropriate immune system response to an acute injury or illness that is helpful for healing.
Acute inflammation is also an important defense against pathogens (harmful bacteria, parasites or viruses).
Your immune system’s ability to mount an adequate and appropriate inflammatory response is critical for survival! As an example, if you were to cut open your hand, causing a large open wound; you don’t want to have excessive bleeding or get an infection. When acute inflammation takes place due to this trauma—it helps you to clot—stopping the bleeding or decreasing the bleeding. It also takes care of pathogens that there is no longer a barrier against—so you don’t get an infection and then helps to heal your open wound. All which is appropriate and necessary! A balanced immune system is self-limited, beneficial and necessary!
Just to summarize, a balanced immune can identify potentially harmful pathogens or substances, recognize self, assess potential level of threat posed by infectious, toxic or non-self antigens and repair any damage that happens when the immune system takes care of threats.
What about Chronic Inflammation or an Unbalanced Immune System ?
Chronic inflammation happens when there is loss of balance of the immune system causing constant inflammation and destruction to your body.
Long term or chronic inflammation can lead to long term problems such as obesity, thyroid issues, autoimmune conditions, diabetes, heart disease and so much more!
Your immune system is no longer regulated and is out of control!
What are some ways gut issues lead to chronic inflammation?
- Issues with digestion . One of the most common digestive problems is not making enough stomach acid. Are you taking any medications that decrease stomach acid such as proton pump inhibitors (omeprazole, esomeprazole, lansoprazole) or H2 blockers (ranitidine, famotidine, cimetidine)?
- Remember that stomach acid is important for helping with the breakdown of food and killing pathogens such as bacteria, fungus & parasites.
- If you are not making enough stomach acid to help with the break down of food and also let bad bacteria, fungus or parasites survive to hang out in your intestines, which wreaks havoc & causes inflammation!
2 . Leaky Gut also known as intestinal hyperpermeability. This is when the intestinal lumen no longer has tight junctions between your cells. This means that the physical barrier between the digestive tract and blood stream is broken down; making it easy for intestinal contents to enter the blood stream.
- Your immune system will see things that it is not suppose to, such as big food particles, which causes your immune system to react. This can then lead to food sensitivities for example.
- Your immune system will also be exposed to more pathogens.
How Does Leaky Gut Happen?
- NSAIDs such as ibuprofen, steroids, and naproxen. Research shows that NSAIDs cause small intestinal inflammation causing leaky gut and can also be toxic to the cells of your gut.
- Viral, bacterial or protozoan infections
- Gluten
- Inflammation
- Stress
- Cytotoxic drugs
- Xenobiotics such as glyphosate which alters the gut microbiome
- Heavy metals such as mercury
- Antibiotics which alter the microbiome
- Standard American Diet
Chronic Health Issues associated with gut health : If your gut is ticked off, your immune system is gonna be ticked off, causing chronic inflammation that affects your whole body!
Everyone has different genetics and environmental factors, which can lead to a different path of chronic issues you are faced with!
Obesity . Defined as “accumulation of abnormal or excessive fat that may interfere with the maintenance of an optimal state of health.” In the U.S. the population with obesity is 42.2%. There is not any up to date costs for obesity, but in 2008 the estimated annual cost was $147 billion dollars. This was 12 years ago, and now the percentage of obesity has increased from 2008. Can you imagine what the annual cost is now?
Chronic inflammation causes an increase in certain inflammatory mediators (such as TNF-alpha, IL-6) which can lead to inflammation in fat cells (adipose tissue).
Did you know that fat cells (white adipose tissue) is an active participant in regulating your immune system and play a role in inflammation?
Fat cells (adipose tissue) that are exposed to chronic inflammation initially from the gut can then go on to produce more inflammation, which ends up becoming a vicious cycle.
When fat cells become enlarged, the blood supply to these cells may be decreased leading to a limited blood supply to this tissue. When this happens, fat cells or tissue begin to die, which leads to more production of inflammatory mediators! This then leads to overall inflammation in the body that is linked to:
- Abdominal obesity
- Metabolic abnormalities that lead to altered cholesterol and sugar metabolism
- Atherosclerosis than can lead to heart attacks and stroke
- Insulin resistance
- Diabetes
- High blood pressure
Thyroid issues. To really understand why thyroid problems are a big deal, first we must understand the importance of a well functioning thyroid. The thyroid is a small, butterfly-shaped gland located at the base of the neck. It may be small, but it is powerful and plays a vital role in how your body functions! The thyroid can influence all the parts of your body such as your gut, heart, brain, liver, kidneys and much, much more!
Your thyroid needs proper fuel or nutrients to produce thyroid hormone to be able to influence the rest of your body.
The thyroid gland mostly produces T4 (thyroxine) and some T3 (triiodothyronine) that is made up of iodine and tyrosine. T4 contains four iodine atoms and T3 contains three iodine atoms. Conversion of T4 to T3 takes place mostly outside of the thyroid gland. Most of the body responds & recognizes T3.
If the gut is in poor condition, such as a leaky gut, it is going to be difficult to get nutrient absorption to take place from the gut into the rest of the body. The thyroid suffers and does not get all the vital nutrients such as iodine and selenium for proper functioning.
Why else is having a healthy gut important for your thyroid health?
- 20% of the conversion of T4 to T3 happens in the gut!
- Healthy gut microbes can convert T4 to T3.
- Bile acids when secreted into the small intestine following fat consumption increase activity of the enzyme that converts T4 to T3.
Hashimoto’s is an autoimmune disease that affects more women than men. Hashimoto’s is a chronic inflammatory state in which the immune system makes antibodies that attack the thyroid gland. This then damages the thyroid, and if left untreated, can lead to the thyroid not making enough thyroid hormones. If found and treated early, most individuals with Hashimoto’s will not need to be on thyroid replacement medication.
Autoimmune Conditions can occur other places in the body, not just the thyroid. Autoimmune conditions are a result of the immune system attacking the body’s own organs, tissues and cells.
- Affects 23.5 million U.S. citizens
- Leading cause of death & disability
- More than 80 diseases are associated with autoimmune conditions
- Most common: Hashimoto’s, Lupus, Inflammatory Bowel Disease, Rheumatoid Arthritis, Multiple Sclerosis, Type 1 Diabetes, Grave’s Disease, Celiac disease
- Inflammatory bowel disease is chronic inflammation of the GI tract. Prolonged inflammation results in damage to the GI tract. Two types of IBD: Crohn’s disease and ulcerative colitis. Crohn’s disease can affect all parts of the GI tract—mouth to anus. Inflammation may include multiple layers of the walls of the GI tract. Ulcerative colitis affects the large intestine and rectum. Damage is usually patchy. Inflammation is usually present in the innermost layer of the lining of the colon.
Chronic inflammation from leaky gut can also cause seasonal allergy symptoms to be out of control!
Six STEPS to a Healthy Gut & Balanced Immune System:
- Eat a clean, well-balanced diet
- Eat earth made foods. Earth made foods don’t need labels! Try to eat a rainbow of colors in regards to produce to get all your nutrients—each color has different minerals, vitamins etc.
- Stay away from processed foods such as soda and box foods that can cause inflammation. If you are reading ingredients labels and see a big, long word that you have no idea how to pronounce or what it is, your body likely has no idea what it is either, so your immune system mounts a response causing inflammation!
- Buy organic foods. If the budget does not allow for all organic foods, buy all the produce that are listed under the Dirty Dozen organic. The Environmental Working Group has a list of produce with the highest pesticide/herbicide contents: www.EWG.org (strawberries, spinach, kale, nectarines, apples, grapes, peaches, cherries, pears, tomatoes, celery, potatoes, and hot peppers).
2. Stay well-hydrated with water
- Most of your body is made up of water and needs water to work effectively and also flush out toxins.
- In general, drinking 1/2 your weight in ounces per day is enough. For example, a 150 lb person needs ~75 oz of water daily. You may need more water if you are out in the sun or exercising vigorously!
- Also something to consider is how your water rate? What is your water source? How clean is your water? Have you considered filtered water?
3. Rest
- Are you getting quality sleep at night?
- How many hours of sleep do you get at night?
- Do you wake up well rested?
- Sticking to a schedule can be very helpful: going to bed and getting up at the same time everyday.
4. Self care
- Are you taking time daily for yourself?
- Are you taking time to rest and let your body reset?
- Are you taking time for movement or exercise?
- Self care looks different for everyone. Self care is a way for you to relax and do something you enjoy!
5. De-Stress
- This is a part of self care. You need to find ways to stay calm and relaxed.
- Chronic stress all by itself causes inflammation!
- If you have trouble taking time for yourself here are some tips: put self care on your daily schedule—even if it is for 2-5 minutes to start out. Have an accountability partner to make sure you are not ignoring your scheduled self care!
6. Supplements
- Multivitamin: basic minerals and vitamins that your entire body needs to function daily.
- Omega 3’s: anti-inflammatory for your gut and whole body. Your body needs omega 3’s to make cell membranes, make hormones and fuel your brain.
- Probiotics: improve gut health—digestion, absorption and microbiome. Also helps to improve immune health.
Having gut issues or an out of whack immune system? Need a partner in your health journey? Schedule a FREE 15 minute strategy call with New Beginnings. Email Staff@NewBeginningsFMC.com or call 970-305-0101 to schedule.
References:
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4566439/--role of gut microbiome
- https://depts.washington.edu/ceeh/downloads/FF_Microbiome.pdf--human microbiome
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5507106/
- https://www.cdc.gov/obesity/data/adult.html
- https://journal-inflammation.biomedcentral.com/articles/10.1186/1476-9255-9-1
- https://www.niaid.nih.gov/diseases-conditions/autoimmune-diseases
- https://www.womenshealth.gov/a-z-topics/autoimmune-diseases
- https://www.cdc.gov/ibd/what-is-IBD.htm
- https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/inflammatory-bowel-disease/symptoms-causes/syc-20353315?p=1
- https://www.hsph.harvard.edu/nutritionsource/what-should-you-eat/fats-and-cholesterol/types-of-fat/omega-3-fats/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/16829066
- https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/articles/7041-the-structure-and-function-of-the-digestive-syst...
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/20351569
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/12269922
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/1555538
- https://academic.oup.com/intimm/article/8/2/231/671078
- https://ec.bioscientifica.com/view/journals/ec/6/4/R52.xml
- https://academic.oup.com/jcem/article/92/11/4180/2598186
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK279393/
- http://www.vivo.colostate.edu/hbooks/pathphys/digestion/basics/gi_immune.html
- https://www.thyroid.org/hypothyroidism/
- https://www.thyroid.org/hyperthyroidism/
- https://www.health.harvard.edu/vitamins-and-supplements/health-benefits-of-taking-probiotics